一杯咖啡的时间 上手 Redux & Redux Toolkit
当前字数: 0 字 阅读时长: 0 分钟
Redux
Redux 是一个管理全局应用状态的库。
概念
State 管理
这是一个包含以下部分的 React 计数器组件:
- state:驱动应用的真实数据源头。
- view:基于当前状态的视图声明性描述。
- actions:根据用户输入在应用程序中发生的事件,并触发状态更新。
jsxfunction Counter() { // State: counter 值 const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0); // Action: 当事件发生后,触发状态更新的代码 const increment = () => { setCounter((prevCounter) => prevCounter + 1); }; // View: 视图定义 return ( <div> Value: {counter} <button onClick={increment}>Increment</button> </div> ); }如果当有多个组件需要共享和使用相同
state时,会变得很复杂,有时可以通过提升 state到父组件解决。当组件关系复杂庞大时,这并不是一个好方法。解决这个问题的一种方法是从组件中提取共享
state,并将其放入组件树之外的一个集中位置。这样,我们的组件树就变成了一个大view,任何组件都可以访问state或触发action,无论它们在树中的哪个位置。通过定义和分离
state管理中涉及的概念并强制执行维护view和state之间独立性的规则,代码变得更结构化和易于维护。这就是
Redux背后的基本思想:应用中使用集中式的全局状态来管理,并明确更新状态的模式,以便让代码具有可预测性。
Immutability 不可变性
"Mutable" 意为 "可改变的",而 "immutable" 意为永不可改变。
Redux期望所有状态更新都是使用不可变的方式(Immutability)。JavaScript的对象(object)和数组(array)默认都是mutable的:
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };
// 对外仍然还是那个对象,但它的内容已经变了
obj.b = 3;
const arr = ["a", "b"];
// 同样的,数组的内容改变了
arr.push("c");
arr[1] = "d";Redux 术语
State,Actions,和Reducers是Redux的构建模块。每个Redux应用都有state值,创建actions来描述发生的事情,并使用reducer函数根据之前的state和action计算新的状态值。
Actions
action 是一个带有 type 并且描述发生了什么的普通对象:
const addTodoAction = { type: "counter/increment", payload: "ok ok" };- type: 字符串。用来描述
action。通常写为域/事件名称feature/eventName。 - payload: 通常用用描述发生的事情的附加信息。
- 操作应该包含描述发生的事情所需的最少数据量。
Reducers
(state, action) => newState。
Reducers 函数。接收当前的 state 和一个 action。通常用于决定如何更新状态,并返回新状态:
const initialState = { value: 0 };
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
if (action.type === "counter/increment") {
return { ...state, value: state.value + 1 };
}
return state;
}Reducer 必需符合以下规则:
- 仅使用
state和action参数计算新的状态值。 - 禁止直接修改
state。总是返回一个副本。来做不可变更新(immutable updates)。 - 禁止任何异步逻辑、依赖随机值或导致其他 “副作用” 的代码。
在 Redux 中,我们的 reducer 永远不允许改变原始/当前状态值!
// ❌ 非法 - 默认情况下,这会改变状态!
state.value = 123;Reducers 只能 复制 原始值,并只能改变这些副本。
// ✅ 做了复制,所以是安全的
return { ...state, value: 123 }拆分/组合 Reducers
Redux 应用程序实际上只有一个 reducer 函数 root reducer 传递给 createStore 函数。
Redux reducer 通常根据更新的 Redux state 部分进行拆分:
import todosReducer from "./features/todos/todosSlice";
import filtersReducer from "./features/filters/filtersSlice";
export default function rootReducer(state = {}, action) {
// 返回一个新的根 state 对象
return {
// `state.todos` 的值是 todos reducer 返回的值
todos: todosReducer(state.todos, action),
// 对于这两个 reducer,我们只传入它们的状态 slice
filters: filtersReducer(state.filters, action),
};
}导入并使用 combineReducers :
combineReducers 接受一个对象,其中键名将成为根 state 对象中的键,值是描述如何更新 Redux 状态的 slice reducer 函数。
你给 combineReducers 的键名决定了你的状态对象的键名是什么!
import { combineReducers } from "redux";
import todosReducer from "./features/todos/todosSlice";
import filtersReducer from "./features/filters/filtersSlice";
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
// 定义一个名为`todos`的顶级状态字段,由`todosReducer`处理
todos: todosReducer,
filters: filtersReducer,
});
export default rootReducer;Store
当前 Redux 应用的状态存在于一个名为 store 的对象中。 store 是通过传入一个 reducer 来创建的。
import { createStore } from "redux";
import rootReducer from "./reducer";
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
export default store;Redux store汇集了构成应用程序的state、actions和reducers:- 在内部保存当前应用程序
state - 通过
store.getState()访问当前state; - 通过
store.dispatch(action)更新状态; - 通过
store.subscribe(listener)注册监听器回调; - 通过
store.subscribe(listener)返回的 unsubscribe 函数注销监听器。
- 在内部保存当前应用程序
Store enhancers让我们能够在创建store时进行自定义操作Enhancers包装了store并且可以覆盖它的方法createStore接受一个enhancer作为参数- 可以使用
compose API将多个enhancers合并在一起
Middleware是自定义store的主要方式- 使用
applyMiddleware enhancer添加middleware Middleware被写成三个相互嵌套的函数- 每次
dispatch action时都会运行middleware Middleware内部可能有副作用
- 使用
Redux Store
Redux 应用程序中只有一个 store。当你想要拆分数据处理逻辑时,你将使用 reducer composition 并创建多个可以组合在一起 reducer,而不是创建单独的 store。
Dispatch
Redux store 有一个方法叫 dispatch。更新 state 的唯一方法是调用 store.dispatch() 并传入一个 action 对象。
store.dispatch({ type: "counter/incremented" });
store.dispatch({ type: "counter/incremented", payload: "Learn about stores" });dispatch 一个 action 可以形象的理解为 "触发一个事件"。每次我们调用 store.dispatch(action) 时:
store调用rootReducer(state, action)。store将新的state保存在里面。store调用所有的监听器订阅回调。- 监听器现在通过调用
store.getState()来访问store并读取最新的state。
Selectors
Selector 函数可以从 store 状态树中提取指定的片段。
const selectCounterValue = (state) => state.value;
const currentValue = selectCounterValue(store.getState());Redux 原则
单一数据源
- 应用程序的全局状态作为对象存储在单个
store中。任何给定的数据片段都应仅存在于一个位置,而不是在许多位置重复。
State 是只读的
- 更改状态的唯一方法是
dispatch一个action,这是一个描述所发生事件的对象。
使用 Reducer 纯函数进行更改
- 若要指定如何基于
action更新状态树,请编写reducer函数。 - 与任何其他函数一样,你可以将
Reducer拆分为较小的函数以帮助完成工作,或者为常见任务编写可重用的Reducer。
Redux 数据流
单向数据流(one-way data flow)
- 用
state来描述应用程序在特定时间点的状况。 - 基于
state来渲染出View。 - 当发生某些事情时(例如用户单击按钮),
state会根据发生的事情进行更新,生成新的state。 - 基于新的
state重新渲染View。
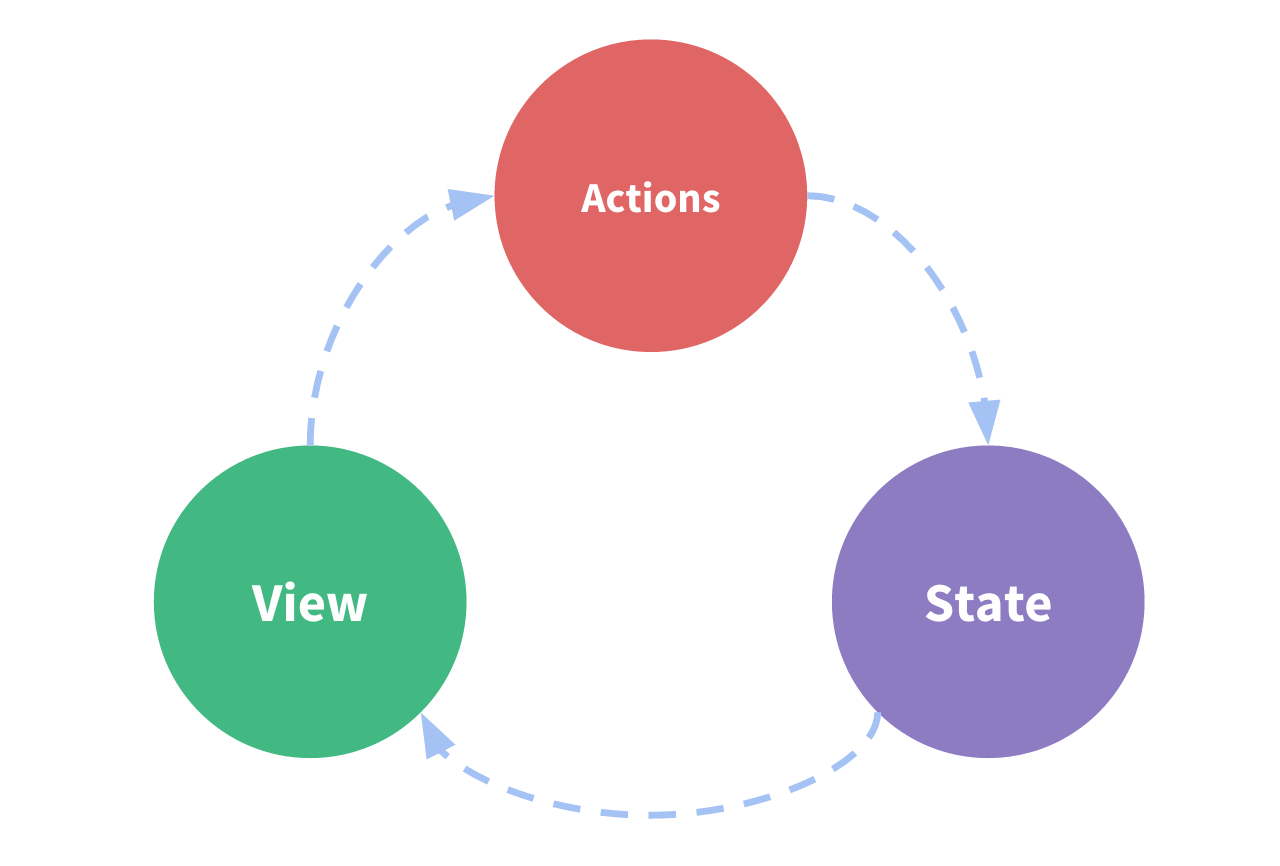
Redux 数据流
Redux 使用 "单向数据流",可以将这些步骤分解为更详细的内容:
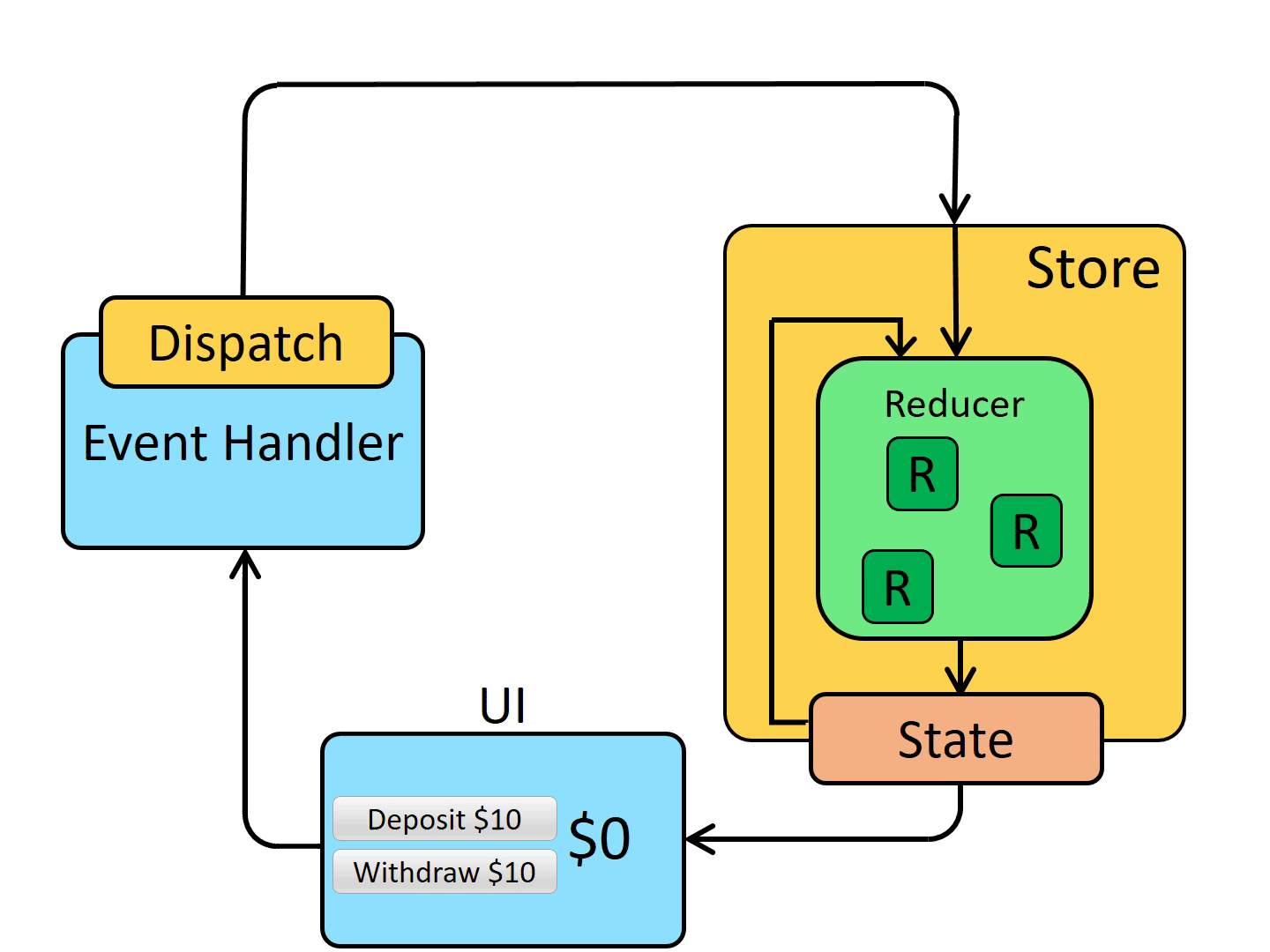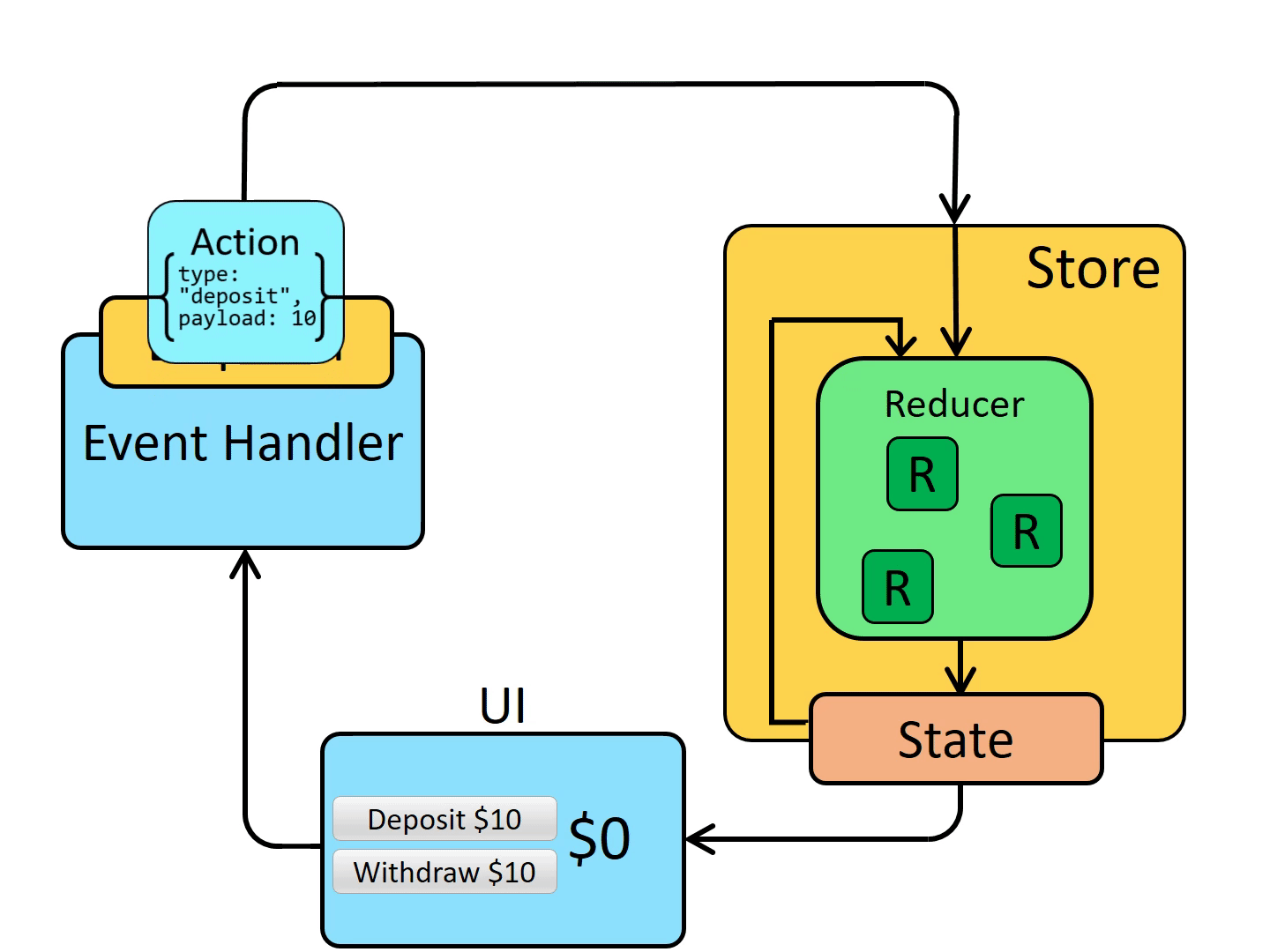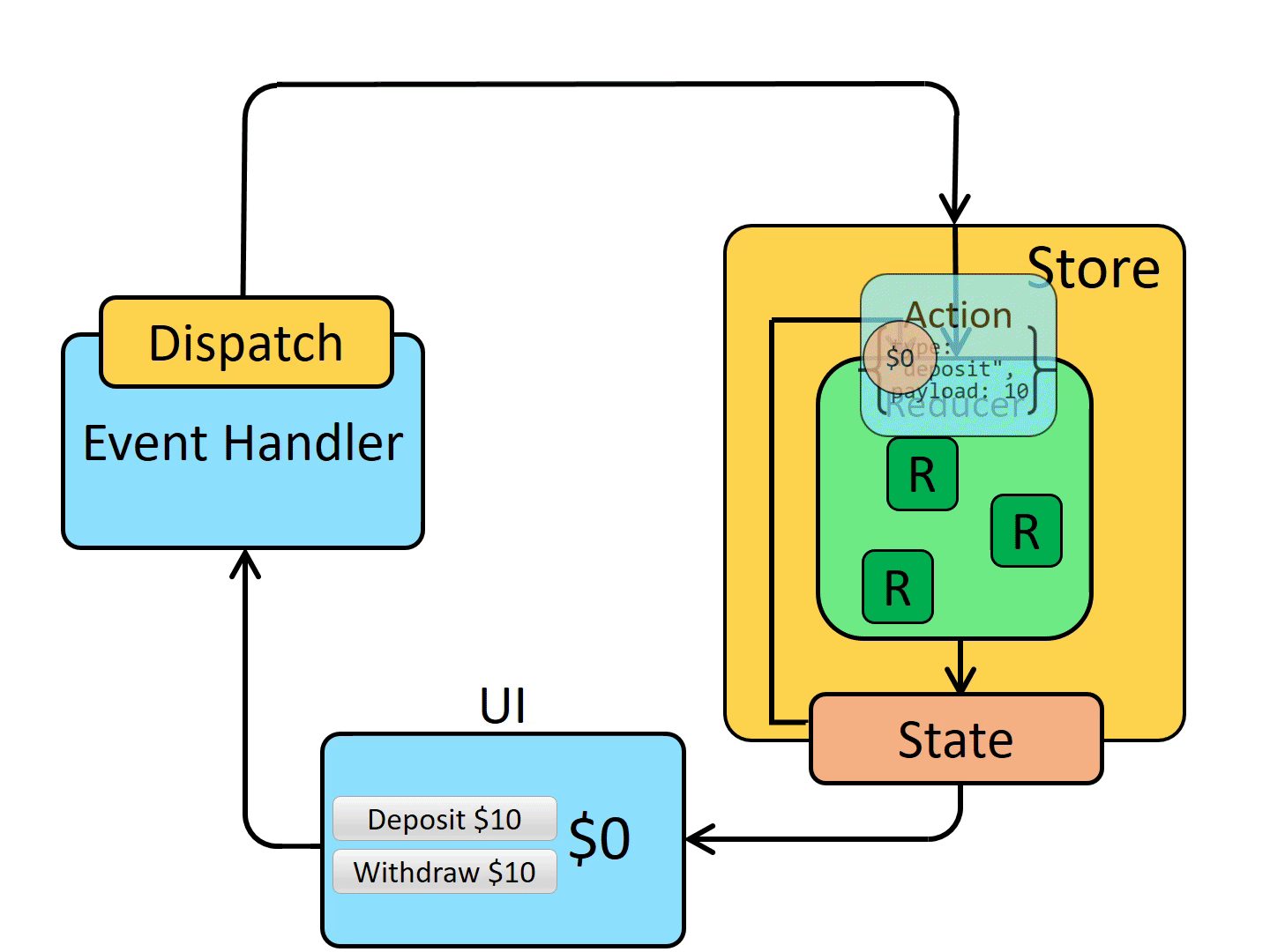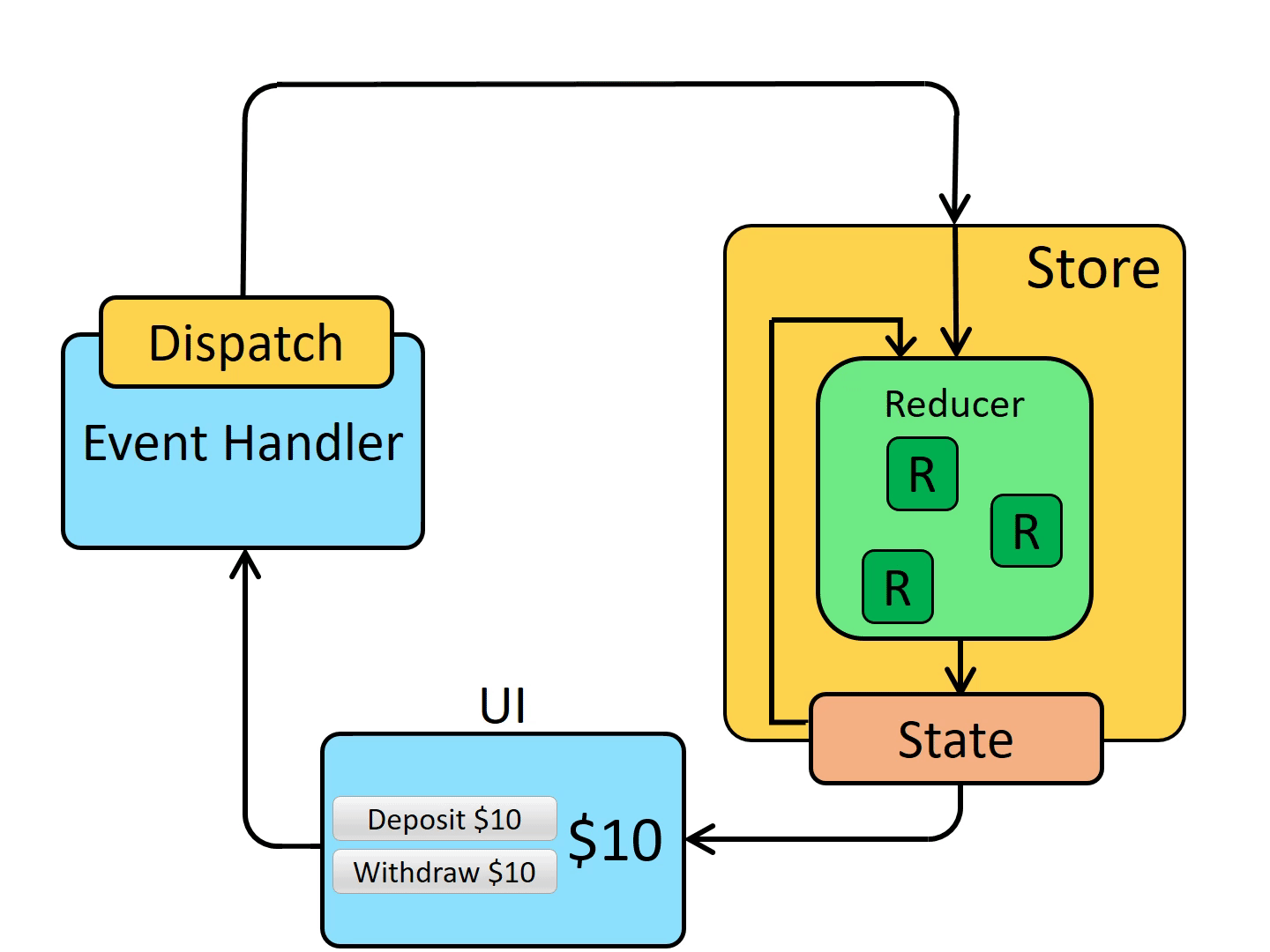
初始启动:
- 使用最顶层的
root reducer函数创建Redux store store调用一次root reducer,并将返回值保存为它的初始state- 当
UI首次渲染时,UI组件访问Redux store的当前state,并使用该数据来决定要呈现的内容。 - 同时监听
store的更新,以便他们可以知道state是否已更改。
- 使用最顶层的
更新环节:
- 应用程序中发生了某些事情,例如用户单击按钮
dispatch一个action到Redux store,例如dispatch({type: 'counter/increment'})store用之前的state和当前的action再次运行reducer函数,并将返回值保存为新的statestore通知所有订阅过的UI,通知它们store发生更新- 每个订阅过
store数据的UI组件都会检查它们需要的state部分是否被更新。 - 发现数据被更新的每个组件都强制使用新数据重新渲染,紧接着更新网页。
<body>
<div>
<span id="value">0</span>
<button id="increment">+10</button>
<button id="decrement">-10</button>
</div>
<script type="module">
import { createStore } from "https://unpkg.com/redux@latest/dist/redux.browser.mjs";
// 定义State: 定义一个初始状态值
const initialSate = { value: 0 };
// 定义Reducer: 参数接收 state(初始值initialSate) 和 action
const reducer = (state = initialSate, action) => {
// / Reducers 通常会查看发生的 action 的 type 来决定如何更新状态
switch (action.type) {
case "counter/incremented":
return { value: state.value + 10 };
case "counter/decremented":
return { value: state.value - 10 };
default:
return state;
}
};
// 创建Store:调用 Redux 库 createStore 来创建一个 store 实例
// createStore 会执行一次 reducer,对 state 进行初始化
const store = createStore(reducer);
// 获取 HTML 元素
const valueEl = document.getElementById("value");
// 获取 Store 状态并更新 UI
function render() {
const state = store.getState();
valueEl.innerHTML = state.value.toString();
}
// 初始化调用 更新 UI
render();
// 订阅 Store 的状态
store.subscribe(render);
// 点击按钮时 发起 action
document.getElementById("increment").addEventListener("click", function () {
store.dispatch({ type: "counter/incremented" });
});
document.getElementById("decrement").addEventListener("click", function () {
store.dispatch({ type: "counter/decremented" });
});
</script>
</body>
Redux Toolkit
官方推荐的编写 Redux 逻辑的方法(最佳实践)也称为 "RTK"。
为什么要用 redux-toolkit 而不是 redux
- 配置一个 Redux store 过于复杂。
- Redux Toolkit (RTK) 是编写 Redux 逻辑的标准方式。
- Redux 需要太多的样板代码。
- 围绕 Redux 核心,并包含其他有用的包.
configureStore
configureStore用来设置一个具有良好默认值的Redux store。Redux Toolkit的configureStore API,可简化store的设置过程。toolkit其实只是对redux进行了封装,实际上store和redux中的是一样的。
import { configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
import todosReucer from "./features/todos/todosSlice";
import filtersReducer from "./features/filters/filtersSlice";
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
// 定义一个名为 `todos` 的顶级 state 字段,值为 `todosReducer`
todos: todosReducer,
filters: filtersReducer,
},
});
export default store;configureStore 为我们完成了所有工作:
- 自动组合 slice reducers 来创建根 reducer
- 自动添加更多
middleware来检查常见错误,例如意外改变(mutate)state - 自动设置
Redux DevTools扩展连接
createSlice
createSlice简化了Redux actions和reducers的编写根据
slice/reducer名称自动生成action creatorsReducers可以使用Immer在createSlice中“改变”(mutate)state
import { createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
const initialState = {
entities: [],
status: null,
};
const todosSlice = createSlice({
name: "todos",
initialState,
reducers: {
todoAdded(state, action) {
// ✅ “突变”(mutate)代码在 createSlice 中是可以的!
state.entities.push(action.payload);
},
todoToggled(state, action) {
const todo = state.entities.find((todo) => todo.id === action.payload);
todo.completed = !todo.completed;
},
todosLoading(state, action) {
return {
...state,
status: "loading",
};
},
},
});
export const { todoAdded, todoToggled, todosLoading } = todosSlice.actions;
export default todosSlice.reducer;createSlice接收一个包含三个主要选项字段的对象:name:一个字符串,将用作生成的action types的前缀initialState:reducer的初始statereducers:一个对象,其中键是字符串,值是处理特定actions的case reducer函数
createAsyncThunk
createAsyncThunk为异步调用生成thunkdispatch thunk运行payload creator并dispatch actions- 可以在
createSlice.extraReducers中处理thunk actions
createAsyncThunk接收两个参数:- 一个字符串,用作生成的
action types的前缀 - 一个
payload creator回调函数,应该返回一个Promise。这通常使用async/await语法编写,因为async函数会自动返回一个Promise。
- 一个字符串,用作生成的
import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
// 省略 imports 和 state
export const fetchTodos = createAsyncThunk("todos/fetchTodos", async () => {
const response = await client.get("/fakeApi/todos");
return response.todos;
});
const todosSlice = createSlice({
name: "todos",
initialState,
reducers: {
// 省略 reducer cases
},
extraReducers: (builder) => {
builder
.addCase(fetchTodos.pending, (state, action) => {
state.status = "loading";
})
.addCase(fetchTodos.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
const newEntities = {};
action.payload.forEach((todo) => {
newEntities[todo.id] = todo;
});
state.entities = newEntities;
state.status = "idle";
});
},
});
// 省略 exportscreateEntityAdapter
createEntityAdapter 为标准化 state 提供了 reducers + selectors
- 自动生成一个
thunk + pending/fulfilled/rejected action creators - 包括用于常见任务的
reducer功能,例如添加/更新/删除items - 为
selectAll和selectById生成记忆化selectors
Redux 内部实现
Redux 的 API 非常少。Redux 为你定义了一系列的约定(例如 reducers),同时提供了少量的辅助函数来把这些约定整合到一起。
顶级暴露的方法:
createStore(reducer, [preloadedState], [enhancer])combineReducers(reducers)applyMiddleware(...middlewares)bindActionCreators(actionCreators, dispatch)compose(...functions)。
Store API:
getState()dispatch(action)subscribe(listener)replaceReducer(nextReducer)
以下代码实现的测试都基于该计数器代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Redux basic example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<span id="value">0</span>
<button id="increment">+10</button>
<button id="decrement">-10</button>
</div>
<script type="module">
import { createStore } from "https://unpkg.com/redux@latest/dist/redux.browser.mjs";
// 定义State: 定义一个初始状态值
const initialSate = { value: 0 };
// 定义Reducer: 参数接收 state(初始值initialSate) 和 action
const reducer = (state = initialSate, action) => {
// / Reducers 通常会查看发生的 action 的 type 来决定如何更新状态
switch (action.type) {
case "counter/incremented":
return { value: state.value + 10 };
case "counter/decremented":
return { value: state.value - 10 };
default:
return state;
}
};
// 创建Store:调用 Redux 库 createStore 来创建一个 store 实例
const store = createStore(reducer);
// 获取 HTML 元素
const valueEl = document.getElementById("value");
// 获取 Store 状态并更新 UI
function render() {
const state = store.getState();
valueEl.innerHTML = state.value.toString();
}
// 初始化调用 更新 UI
render();
// 订阅 Store 的状态
store.subscribe(render);
// 点击按钮时 发起 action
document
.getElementById("increment")
.addEventListener("click", function () {
store.dispatch({ type: "counter/incremented" });
});
document
.getElementById("decrement")
.addEventListener("click", function () {
store.dispatch({ type: "counter/decremented" });
});
</script>
</body>
</html>实现 createStore
store内部有当前的stategetState方法返回当前state值dispatch调用reducer,保存state,并运行监听器store在启动时dispatch一个action来初始化reducers的statestore API是一个对象,里面有 {dispatch,subscribe,getState}
function createStore(reducer) {
// store 内部 state 值
let state;
// store 内部保存监听器集合
let listerners = [];
// `getState` 方法返回当前 `state` 值
function getState() {
return state;
}
// dispatch 调用 reducer,保存 新的 state。
// dispatch 运行 subscribe 订阅的 集合中 所有函数
function dispatch(action) {
state = reducer(state, action);
listerners.forEach((listerner) => listerner());
}
// subscribe 用来 订阅 发布函数,可以多个订阅放入集合中。
function subscribe(listener) {
listerners.push(listener);
}
// 内部启动时触发一次 dispatch
dispatch({ type: "@@redux/init" });
const store = { getState, dispatch, subscribe };
// 返回 { dispatch, subscribe, `getState }
return store;
}- 测试:
<!-- ... 省略以上代码 ... -->
<!-- 引入自己实现的 createStore -->
<script src="./redux-test.js"></script>
<script type="module">
// 使用 redux-test.js 中的 createStore
// import { createStore } from "https://unpkg.com/redux@latest/dist/redux.browser.mjs";
// ... 以下省略代码 ...
</script>
<!-- ... 省略以下代码 ... -->实现 combineReducers
combineReducers就是把多个reducer,合并成一个reducer函数,传递给createStore使用。- 参数:一个
reducers对象,对象的value对应不同的reducer。 - 返回:调用了
reducers对象里所有reducer后的一个reducer函数,并且构造一个与reducers对象结构相同的state对象。
function combineReducers(reducers) {
// 获取传入对象的所有 key
const reducersKeys = Object.keys(reducers);
// 返回的一个reducer createStore 就接受一个 reducer 函数
const finalReducer = (state = {}, action) => {
const finalState = {};
// 遍历执行 reducers 中 所有的 reducer
for (let i = 0; i < reducersKeys.length; i++) {
// 当前key
const key = reducersKeys[i];
// 当前的 reducer
const currentReducer = reducers[key];
// 执行当前的 reducer 传入 finalReducer 的参数
const currentState = currentReducer(state[key], action);
// 利用传入的对象结构 构造一个结构相同的新 state 返回
finalState[key] = currentState;
}
return finalState;
};
return finalReducer;
}- 测试:
// ... 省略以上代码 ...
// 定义State: 定义一个初始状态值
const initialSate = { value: 0 };
// 定义Reducer: 参数接收 state(初始值initialSate) 和 action
const reducer = (state = initialSate, action) => {
// / Reducers 通常会查看发生的 action 的 type 来决定如何更新状态
switch (action.type) {
case "counter/incremented":
return { value: state.value + 10 };
case "counter/decremented":
return { value: state.value - 10 };
default:
return state;
}
};
// 测试 combineReducers
const todoReducer = (state = "todo", action) => {
return state;
};
const otherReducer = (state = { other: 0 }, action) => {
return state;
};
// 创建Store:调用 Redux 库 createStore 并使用 combineReducers 来创建一个 store 实例
const store = createStore(
combineReducers({ reducer, todoReducer, otherReducer })
);
console.log(store.getState());
// ... 省略以下代码 ...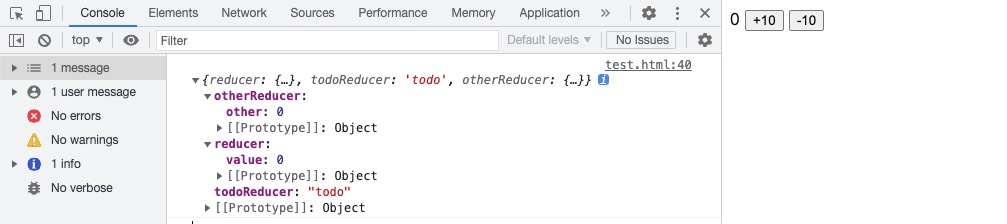
实现 applyMiddleware
middleware 中间件 是什么:
middleware是自定义store的主要方式。middleware中间件是让我们自定义dispatch的函数。middleware在dispatch action和reducer之间提供扩展点。一般用来进行日志记录、崩溃报告、异步 API 通信、路由等。middleware被写成三个相互嵌套的函数 每次dispatch action时都会运行middleware。- 自定义
middleware示例:
// 外层 function:
function logger(storeAPI) {
return function wrapDispatch(next) {
return function handleAction(action) {
console.log("will dispatch", action);
// 调用 middleware 链中下一个 middleware 的 dispatch。
// 或者使用 storeAPI.dispatch(action) 重启管线
const returnValue = next(action);
// 这里也可以使用 storeAPI.getState()
console.log("state after dispatch", storeAPI.getState());
// 一般会是 action 本身,除非后面的 middleware 修改了它。
return returnValue;
};
};
}
// 使用箭头函数:
const anotherLogger = (storeAPI) => (next) => (action) => {
// 当每个 action 都被 dispatch 时,在这里做一些事情
return next(action);
};applyMiddleware 是什么:
Middleware并不需要和createStore绑在一起使用,也不是Redux架构的基础组成部分。- 但它带来的益处让官方认为有必要在
Redux核心中包含对它的支持。 - 虽然不同的
middleware可能在易用性和用法上有所不同,它仍被作为扩展dispatch的唯一标准的方式。 - 参数: 遵循
Redux middleware API的函数。 - 返回: 一个应用了
middleware后的store enhancer。 - 实现
applyMiddleware:
// 首先 createStore 接收一个 enhancer 函数
function createStore(reducer, enhancer) {
// 如果 传入 enhancer, 返回一个 新的 store
if (enhancer && typeof enhancer === "function") {
const newCreateStore = enhancer(createStore);
const newStore = newCreateStore(reducer);
return newStore;
}
// ... 省略以下代码 ...
}
// 定义 applyMiddleware 接收 middleware
function applyMiddleware(middleware) {
// 定义 enhancer 接收一个创建 store 的方法 并返回一个 newCreateStore
function enhancer(createStore) {
// 定义 newCreateStore 接收 reducer
function newCreateStore(reducer) {
// 使用 createStore 创建 store
const store = createStore(reducer);
// 把这个 store 传递给 middleware,也就是测试代码中的 logger的参数
// 这里开始处理 中间件:调用 middleware 传递当前的 store,返回 wrapDispatch
const wrapDispatch = middleware(store);
// wrapDispatch 接收当前的 store 的 dispatch,并返回一个 新的 dispatch
const newDispatch = wrapDispatch(store.dispatch);
// 重写 store 的 dispatch 并返回
return { ...store, dispatch: newDispatch };
}
// enhancer 返回一个 newCreateStore
return newCreateStore;
}
// applyMiddleware 返回一个 enhancer
return enhancer;
}- 测试
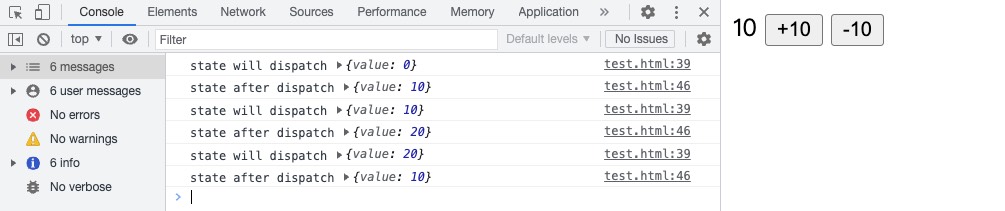
applyMiddleware:
// ... 省略以上代码 ...
// logger middleware
function logger(storeAPI) {
return function wrapDispatch(next) {
return function handleAction(action) {
console.log("state will dispatch", storeAPI.getState());
// 调用 middleware 链中下一个 middleware 的 dispatch。
const returnValue = next(action);
// 这里也可以使用 storeAPI.getState()
// 或者使用 storeAPI.dispatch(action) 重启管线
console.log("state after dispatch", storeAPI.getState());
// 一般会是 action 本身,除非后面的 middleware 修改了它。
return returnValue;
};
};
}
// 测试 applyMiddleware
const store = createStore(reducer, applyMiddleware(logger));
// ... 省略以下代码 ...- 每次
dispatch action时都会运行middleware:
实现 compose
- 想要使用多个
store enhancer,可以使用compose()方法:
// applyMiddleware 中的连续调用:
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(middleware1, middleware2, middleware3)
);
// 或: 这个 store 与 applyMiddleware 和 redux-devtools 一起使用:
const store = createStore(
reducer,
compose(applyMiddleware(thunk), DevTools.instrument())
);- 用来从右到左来组合多个函数。
- 参数:需要合成的多个函数。预计每个函数都接收一个参数。它的返回值将作为一个参数提供给它左边的函数,以此类推。
- 返回:从右到左把接收到的函数合成后的最终函数。
- 函数式编程思想,Redux 中应用很多。
- compose(funcA, funcB, funcC) 形象为 compose(funcA(funcB(funcC())))。
- 实现
compose:
// 定义 compose 函数 接收 需要合成的多个函数
function compose() {
// 接收 函数参数
const funs = [].slice.apply(arguments);
// 接收一个参数 返回一个 从右到左把接收到的函数合成后的最终函数
return function (arg) {
// Array.prototype.reduceRight()
return funs.reduceRight((preFunRes, funItem) => {
return funItem(preFunRes);
}, arg);
};
}- 改写
applyMiddleware支持 多个中间件:
// before : function applyMiddleware(middleware) {
// after: 这里 接收 middlewares
function applyMiddleware(...middlewares) {
function enhancer(createStore) {
function newCreateStore(reducer) {
const store = createStore(reducer);
// before: 这里开始处理 中间件:调用 middleware 传递当前的 store,返回 wrapDispatch
// before: const wrapDispatch = middleware(store);
// after: 循环调用 每个 middleware 并获得返回的 wrapDispatch 队列
const wrapDispatchChain = middlewares.map((item) => item(store));
// befroe: wrapDispatch 接收当前的 store 的 dispatch,并返回一个 新的 dispatch
// before: const newDispatch = wrapDispatch.(store.dispatch);
// after: 使用 compose 从右到左把 wrapDispatchChain 队列中函数 合成最终函数
// after: wrapDispatch 接收当前的 store 的 dispatch,并返回一个 新的 dispatch
const wrapDispatchCompose = compose(...wrapDispatchChain);
const newDispatch = wrapDispatchCompose(store.dispatch);
return { ...store, dispatch: newDispatch };
}
return newCreateStore;
}
return enhancer;
}- 测试
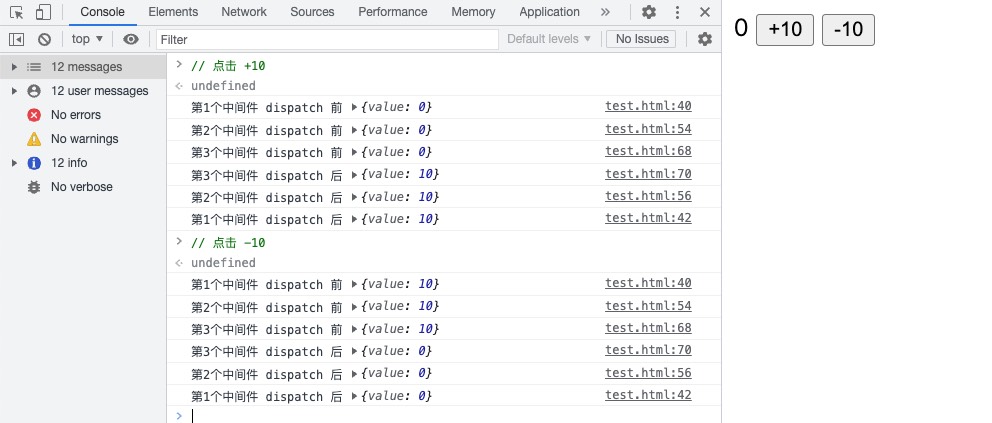
applyMiddleware:
// ... 省略以上代码 ...
// 第一个中间件
function middleware1({ getState }) {
return function wrapDispatch(next) {
return function handleAction(action) {
console.log("第1个中间件 dispatch 前", getState());
const returnValue = next(action);
console.log("第1个中间件 dispatch 后", getState());
return returnValue;
};
};
}
// 第二个中间件
function middleware2({ getState }) {
return function wrapDispatch(next) {
return function handleAction(action) {
console.log("第2个中间件 dispatch 前", getState());
const returnValue = next(action);
console.log("第2个中间件 dispatch 后", getState());
return returnValue;
};
};
}
// 第三个中间件
function middleware3({ getState }) {
return function wrapDispatch(next) {
return function handleAction(action) {
console.log("第3个中间件 dispatch 前", getState());
const returnValue = next(action);
console.log("第3个中间件 dispatch 后", getState());
return returnValue;
};
};
}
// 测试 applyMiddleware
const store = createStore(
reducer,
applyMiddleware(middleware1, middleware2, middleware3)
);
// ... 省略以下代码 ...